重排(回流)reflow与重绘repaint
重排,当DOM元素位置或大小变化时,浏览器需要重新计算元素的几何属性,将元素放到正常的位置,这个过程就是重排。
重绘,当DOM元素的外观发生变化,但没有改变其布局,重新绘制元素外观的过程,叫做重绘。
重排与重绘次数过多会影响页面性能
减少次数方法,将同一元素的布局操作进行一次性改变。如:JS去操作元素top,left,此时就会产生2次。(尽量不要把读操作和写操作放在一个语句里,这样会产生2次或多次的重排重绘)。
对于有动画的元素,使用POSITION的ABSOLUTE或FIXED将其脱离文档,在实现动画时将不会影响到其他元素。
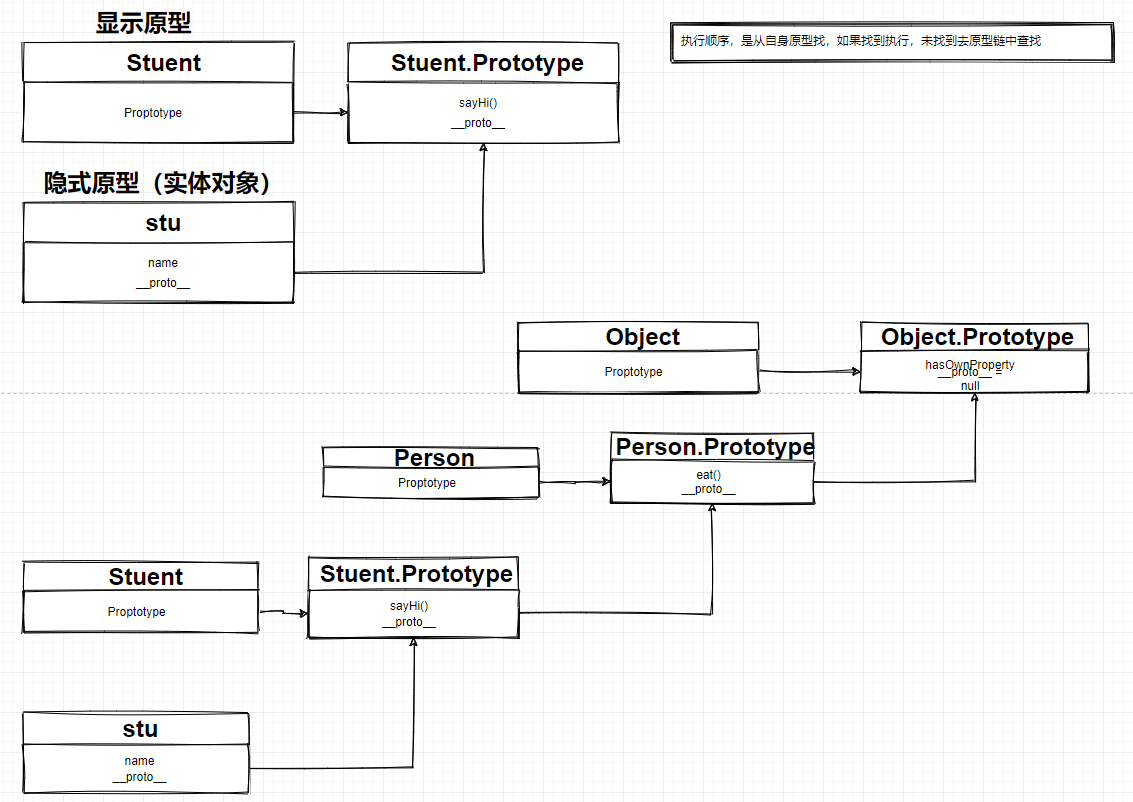
原型
原型是Javascript中继承的基础,JavaScript的继承就是基于原型实现,虽然在ES2015/ES6中有class关键字,但仅是语法糖,最终也是通过原型进行继承。
1
2
3
4function Student(){}
Student.prototype.sayHi=function(){console.log('hi')}
var stu = new Student()如上,定义了一个Student对象,在对象的prototype上定义了一个sayHi方法,当实例化Student对象后,stu实体对象会存在__prto__属性指向Student的Prototype,而Student的Prototype也存在__proto__指向Object的Prototype
继承
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name
}
eat() {
console.log(`${this.name} eat`)
return this
}
}
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name, number){
super(name)
this.number = number
}
sayHi() {
console.log(`${this.name}-${this.number}`)
return this
}
}
class Teacher extends Person{
constructor(name, classes){
super(name)
this.classes = classes
}
sayHi() {
console.log(`${this.name}-classess:${this.classes}`)
return this
}
}
const stu = new Student('student', 22).sayHi().eat()
const tech = new Teacher('teacher', 'c-1').sayHi().eat()
console.log(stu instanceof Student)
console.log(stu instanceof Person)
console.log(stu instanceof Object)
console.log(typeof Student)
console.log(typeof Person)
console.log(Person.prototype === Student.prototype.__proto__
变量及this查找总结
所有自由变量的查找,不是在函数执行时查找,而是在函数定义时查找
this的查找,是在函数执行时查找,而不是在函数定义时查找
EventLoop
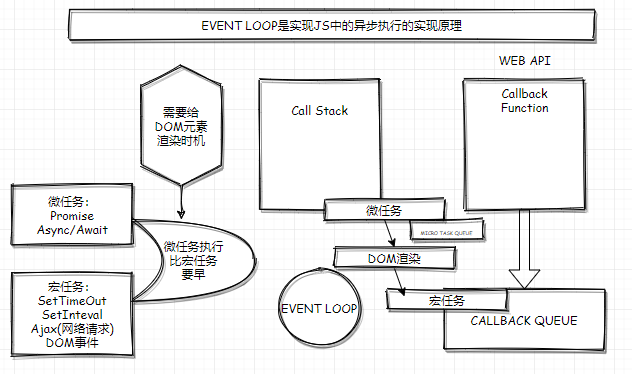
EventLoop是实现JS中的异步执行的实现原理。主要涉及微任务和宏任务。
微任务有Promise,Async/Await。
宏任务有SetTimeOut,SetInteval,Ajax,DOM事件
微任务和宏任务的主要区别是DOM元素渲染时间,微任务执行比宏任务要早示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26// 微任务和宏任务
async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start') //2
await async2() //微任务, 后面都是callback 微任务
console.log('async1 end') //6
}
async function async2(){
console.log('async2') //3
}
console.log('script start') // 1
setTimeout(function(){
console.log('setTimeout') //8
},0)
async1()
new Promise(function(resolve){
console.log('promise1') //4
resolve() // 微任务
}).then(function(){
console.log('promise2') //7
})
console.log('script end') //5AJAX
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
xhr.open('GET','/API', true) // FALSE同步,TRUE是异步
xhr.onreadystatechange = function() {
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status === 200) {
alert(xhr.responseText)
}else{
alert('other')
}
}
}
xhr.send(null)readyState
值 状态 描述 0 UNSET 代理被创建,但尚未调用open()方法 1 OPENED open()方法已经被调用 2 HEADERS_RECEIVED send()方法已经被调用,并且头部和状态已经可获得 3 LOADING 下载中;responseText属性已经包含部分数据 4 DONE 下载操作已完成 status
http请求返回码,1xx 客户端已发送请求,2xx完成,3xx重定向,缓存等(302重定向,304缓存),4xx客户端错误,5xx服务器端错误(504网关请求超时)
防抖和节流
防抖,是触发调频事件后N秒内函数只会执行一次,如果N秒内高频事件再次触发,则生新计算时间
【场景】search搜索联想,用户在不断输入值时,用防抖来节约请求资源
【场景】window触发resize的时候,不断的调整浏览器窗口大小会不断的触发这个事件,用防抖来让其只触发一次1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12function debounce(fn, delay=500) {
let timer = null
return function(){
if(timer){
clearInterval(timer)
}
timer = setTimeout(()=>{
fn.apply(this,arguments)
timer = null
},delay)
}
}节流,高频事件触发,按同样频率进行执行,所以节流会稀释函数执行效率
【场景】鼠标不断点击触发,mousedown(单位时间内只触发一次)
【场景】监听滚动事件,比如是否滑动到底部加载更多1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12function throttle(fn, delay=500){
let timer = null;
return function() {
if(timer){
return
}
timer = setTimeout(()=>{
fn.apply(fn,arguments)
timer = null
},delay)
}
}深度比较
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34const obj1 = {
a: 100, b: {x:100,y:100},c:[1,2,3,4]
}
const obj2 = {
a: 100, b:{x:100,y:100},c:[1,2,3]
}
function isObject(obj) {
return typeof obj === 'object' && obj !==null
}
function isEqual(obj1,obj2) {
if(!isObject(obj1) || !isObject(ob2)) {
return obj1 === obj2
}
if(obj1 === obj2) {
return true
}
const obj1Keys = Object.keys(obj1)
const obj2Keys = Object.keys(obj2)
if (obj1Keys.length !== obj2Keys.length){
return false
}
for(let key in obj1) {
const res = isEqual(obj1[key], obj2[key])
if(!res){
return false
}
}
return true
}
console.log(isEqual(obj1, obj2))数组拍平
方法一
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10function flat(arr) {
const r = arr.some(a=>{
return a instanceof Array
})
if(!r) {
return arr
}
const newArr = Array.prototype.concat.apply([],arr) //重点
return flat(newArr)
}方法二
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11function flat(arr) {
return arr.reduce((newArr,arr)=>{
if(!(arr instanceof Array)) {
newArr.push(arr)
}else{
const newResult = (flat(Array.prototype.concat.apply([],arr))) //重点
newArr = newArr.concat(newResult)
}
return newArr
},[])
}
